Delving into the concept of market volatility, this article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of its different facets, from types to causes and management strategies.
As we unravel the layers of market volatility, we will uncover the key elements that contribute to the fluctuations in financial markets.
What is Market Volatility?
Market volatility refers to the degree of variation or fluctuation in the price of a financial instrument or market index over a specific period of time. It is a measure of how much the price of an asset changes within a given timeframe. High volatility indicates that prices can change dramatically in a short period, while low volatility suggests more stable and predictable price movements.
How is Market Volatility Measured?
Market volatility is commonly measured using statistical metrics such as standard deviation, beta, or the Volatility Index (VIX). Standard deviation calculates the dispersion of a set of data points from its mean, providing a measure of the asset’s price variability. Beta measures the sensitivity of an asset’s returns to the overall market returns, indicating its volatility relative to the market.
VIX, also known as the fear index, gauges the expected volatility in the market based on options pricing.
Factors Contributing to Market Volatility
- Political Events: Elections, geopolitical tensions, and policy changes can create uncertainty and lead to market volatility.
- Economic Data Releases: Reports on indicators like GDP, employment, and inflation can influence market sentiment and trigger volatility.
- Company Earnings: Quarterly earnings reports can significantly impact stock prices and overall market volatility.
- Interest Rates: Changes in interest rates by central banks can affect borrowing costs, investment decisions, and market volatility.
- Market Sentiment: Investor emotions, perceptions, and behavioral biases can drive market volatility, especially during periods of fear or greed.
Types of Market Volatility
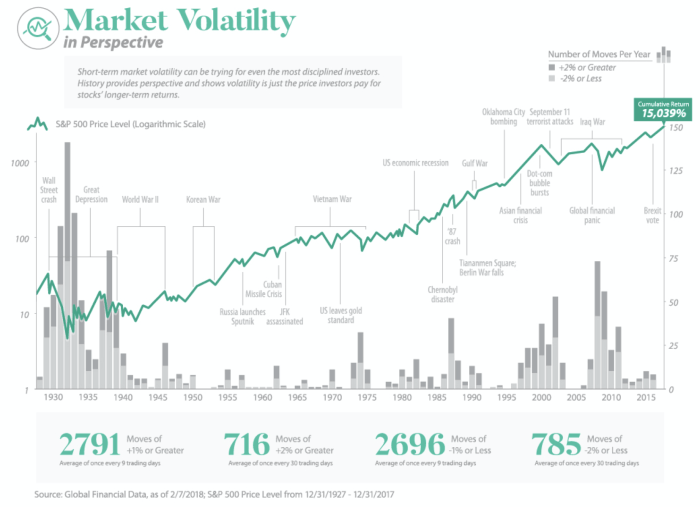
Market volatility can be classified into different types based on various factors. Two significant types are historical volatility and implied volatility, each impacting financial markets differently.
Historical Volatility
Historical volatility refers to the actual price fluctuations of a financial instrument over a specific period. It is calculated based on past market data, providing insights into how much the price has deviated from its average in the past. Traders and investors use historical volatility to assess the risk associated with an asset and make informed decisions.
- Historical volatility is a backward-looking measure that helps in understanding the price movements of an asset.
- It is usually expressed as a percentage and can vary for different securities.
- Higher historical volatility indicates greater price fluctuations, suggesting higher risk.
Implied Volatility
Implied volatility, on the other hand, represents the market’s expectation of future price fluctuations. It is derived from the options market, where the price of options is influenced by expectations of volatility. High implied volatility indicates that market participants anticipate significant price swings in the future.
- Implied volatility is a forward-looking measure that reflects market sentiment and expectations.
- It is not directly observable but can be inferred from option prices using mathematical models like Black-Scholes.
- Changes in implied volatility can impact option prices and overall market sentiment.
Both historical and implied volatility play crucial roles in assessing risk, pricing options, and understanding market dynamics. Traders and investors need to consider both types of volatility to make informed decisions and manage their portfolios effectively.
Causes of Market Volatility

Market volatility can be influenced by various factors that can impact the financial markets. These causes can range from economic indicators to geopolitical events, creating fluctuations in stock prices, exchange rates, and other financial instruments.
Economic Indicators
Economic indicators play a crucial role in determining market volatility. Reports such as GDP growth, unemployment rates, inflation data, and consumer spending can significantly impact investor sentiment and market movements. For instance, a lower-than-expected GDP growth rate can lead to a sell-off in the stock market, while high inflation numbers can trigger fears of rising interest rates, causing markets to become more volatile.
Geopolitical Events
Geopolitical events, such as wars, political instability, trade disputes, and natural disasters, can also influence market volatility. Uncertainty surrounding these events can lead to increased risk aversion among investors, causing fluctuations in asset prices. For example, tensions between countries can result in market sell-offs, as investors seek safer investments in times of geopolitical uncertainty.
Managing Market Volatility
Managing market volatility is essential for investors looking to navigate the ups and downs of the financial markets. By implementing effective strategies, understanding the role of diversification, and utilizing hedging techniques, investors can better protect their investments and reduce the impact of market fluctuations.
Role of Diversification
Diversification is a key strategy in managing market volatility. By spreading investments across different asset classes, industries, and geographic regions, investors can reduce the risk of significant losses during market downturns. This approach helps to cushion the impact of volatility in one sector by potentially benefiting from stability or growth in another.
Using Hedging Techniques
Hedging techniques involve taking positions that offset potential losses in an investor’s portfolio. This can include using options contracts, futures contracts, or inverse ETFs to protect against downside risk. By hedging against market volatility, investors can limit their exposure to sudden market movements and potentially minimize losses.
Market Volatility vs. Risk
Market volatility and investment risk are often used interchangeably, but they actually refer to different concepts in the financial world. Market volatility specifically pertains to the degree of variation in the price of a financial instrument or market index over time, while investment risk encompasses the potential for losses or negative outcomes when investing in a particular asset or portfolio.
Differentiate between Market Volatility and Investment Risk
- Market volatility is a measure of the price fluctuations in the market, while investment risk involves the potential for loss or underperformance of an investment.
- Volatility is a statistical measure that quantifies the dispersion of returns for a given security or market index, whereas risk considers the likelihood of adverse outcomes and the impact on investment goals.
Explain How Market Volatility is Related to Risk Tolerance
Market volatility can significantly impact an investor’s risk tolerance, which is their ability and willingness to endure fluctuations in the value of their investments. Higher volatility often translates to greater risk, as there is a higher chance of experiencing significant gains or losses in a short period. Investors with a low risk tolerance may struggle to handle the uncertainty and potential losses associated with volatile markets, while those with a higher risk tolerance may be more willing to weather the ups and downs in pursuit of greater returns.
Discuss How Investors Can Navigate Volatile Markets While Managing Risk Effectively
- Diversification: Spreading investments across different asset classes can help mitigate risk and reduce exposure to the volatility of any single investment.
- Asset Allocation: Allocating assets based on risk tolerance and investment goals can help investors balance risk and return potential in volatile markets.
- Regular Monitoring: Keeping a close eye on market trends and performance can help investors make informed decisions and adjust their strategies as needed to manage risk effectively.
- Staying Informed: Remaining educated about market conditions, economic indicators, and geopolitical events can help investors anticipate potential risks and opportunities in volatile markets.
In conclusion, understanding market volatility is crucial for investors to navigate turbulent times effectively and make informed decisions to mitigate risks. By grasping the nuances of this phenomenon, one can better prepare for the uncertainties that come with investing in dynamic markets.
Questions and Answers
How do I measure market volatility?
Market volatility is commonly measured using statistical metrics such as standard deviation and beta.
What role does diversification play in managing market volatility?
Diversification helps reduce the impact of market volatility by spreading investments across different asset classes.
Is market volatility the same as investment risk?
Market volatility refers to the fluctuations in prices, while investment risk encompasses the potential loss of capital.




